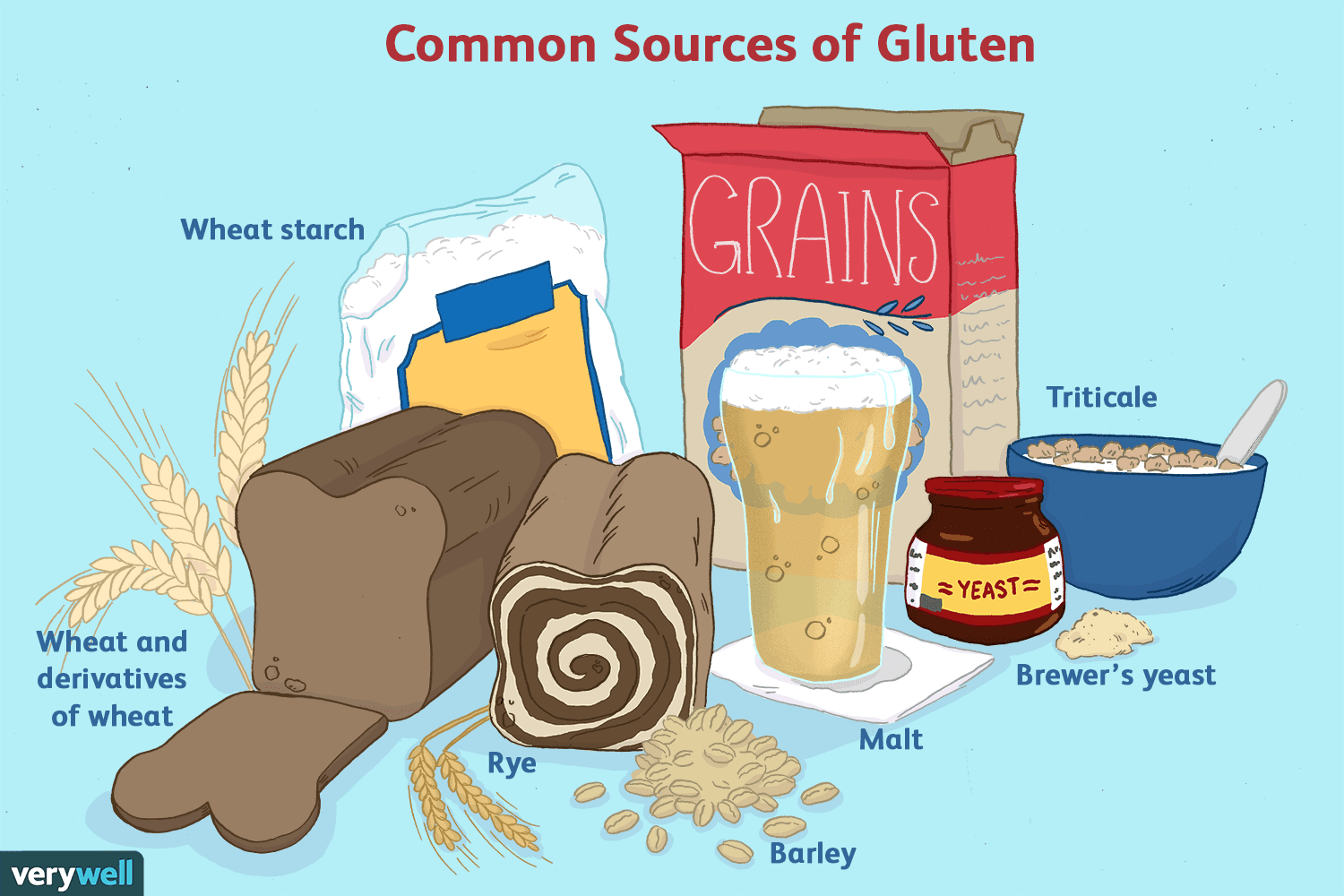
To eat gluten, or not to eat gluten — odds are you have wondered whether or not you should cut out gluten products—anything containing wheat, barley, or rye. (1)
The gluten-free fad has sparked debate among health professionals, arguing the pros and cons of gluten in your diet. Some say cutting out gluten also cuts out a lot of high fiber and nutrient-rich foods too, which means a need to ensure these losses are consumed through other foods. Yet research does show that gluten can cause inflammation and wreak havoc with gut health and can be outright dangerous for those who suffer from celiac disease. (2) (3)
Let’s look at some of the facts on both sides of the argument.
Gluten Pros
Gluten Doesn’t Necessarily Cause Weight Gain
In most situations, gluten doesn’t cause weight gain. In fact, many gluten-free products often contain more carbs and sugar than their glutenous counterparts and could actually add to your waistline. Also — many gluten products have fiber that can satisfy hunger and keep you full which in turn can curb unnecessary snacking and overeating. The key is to find high-quality gluten products that are as free of processing, chemicals, fillers, and preservatives as possible.
Gluten is a Good Source of Carbs and Protein
We all need protein in our diets and some gluten foods provide a good, natural source of protein as part of a healthy diet.
Carbohydrates should make up about 45 percent of a healthy diet, and that’s where gluten is found. Cutting out wheat, rye, barley, and the other grains that provide gluten eliminates some of the key sources of complex carbohydrates needed in a balanced diet. Also lost are the fiber, B vitamins and folate found in carbohydrates, as well as the iron, calcium, and vitamin D provided by fortified breads and cereals.
Gluten Isn’t in All Grains
It’s not uncommon to think that all grains contain gluten. Whole grains are necessary for a healthy, balanced diet, and can help reduce the chance of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. It is important to be well informed and to make sure to get your whole grains from other sources if you choose not to eat gluten products. A key here is to choose whole grains which offer a “complete package” of health benefits and stay away from refined grains, which are stripped of valuable nutrients. Check out amaranth, quinoa, rice, wild rice, buckwheat, millet, and oats. (4)
Gluten Cons
Celiac Disease and Gluten Intolerance
While those with a gluten intolerance and celiac disease can benefit from going gluten-free it is important to know the difference between the two.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that prevents those with it from properly processing and digesting gluten. For them, gluten can cause severe health problems as it triggers the immune system to attack the small intestine. Even trace amounts of gluten can cause significant damage and with repeated attacks, the small intestine loses its ability to absorb vital nutrients like calcium and iron. Over time, those with untreated celiac disease can develop severe nutritional deficiencies, such as osteoporosis and iron-deficiency anemia, as well as other autoimmune disorders, extreme fatigue, infertility, neurological problems. (5)
Gluten sensitivity is not an autoimmune disease. It’s more like lactose intolerance – the inability to process or metabolize lactose – except that it’s gluten that can’t be metabolized.
Those with gluten sensitivity commonly experience gastrointestinal distress when they eat gluten. Those with celiac disease, on the other hand, may experience some of the same symptoms or may have no symptoms at all. (6)
With gluten sensitivity, it doesn’t appear to be as critical to long-term health to avoid gluten – it’s more a matter of choice to avoid symptoms like:
- Bloating
- Abdominal Pain
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Gas
- GERD (gastro-esophageal reflux)
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Bone Pain
- Muscle Pain
- Joint Pain
- Skin rashes/dermatitis
- Weight gain
- Depression
Gluten and Inflammation
If you are dealing with any kind of pain and inflammation, then ditching gluten may be a way to go. (7)
Gliadin is the protein in wheat that can cause an autoimmune reaction in some, where the body begins to attack its own organs; it is also associated with not only celiac disease but also arthritis and fibromyalgia. Studies show that patients with fibromyalgia who eliminated gluten from their diet not only saw a reduction in their joint and muscle pain but also saw improvements in gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms. (8)
1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6625226/
2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5439366/
3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6636598/
4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5310957/
5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6357014/
6) https://gut.bmj.com/content/65/12/1930.full
7) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705319/
8) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02206660




